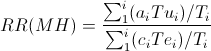The Mantel Haenszel Method
The most popular method used to compute a weighted risk ratio or odds ratio is the Mantel-Haenszel method, which can be used for risk ratios or rate ratios.
From the following table
| Cases | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stratum 1 | Exposed | a1 | Te1 |
| Unexposed | c1 | Tu1 | |
| Total | T1 | ||
| Stratum 2 | Exposed | a2 | Te2 |
| Unexposed | c2 | Tu2 | |
| Total | T2 |
The Mantel Haenszel risk ratio (RRMH) can be computed as follows:
In which: a and c are the number of cases exposed and unexposed in a stratum Te and Tu are the total number exposed and unexposed in a stratum T is the total of a stratum The sums ∑ are calculated for the i strata.
Returning to the example of the cohort study with vaccinated girls and boys:
Crude RR
| Gender | Cases | Total | Attack Rate | RR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | 819 | 1000 | 82% | 4.52 |
| Girls | 181 | 1000 | 18% | ref |
Stratified RRs
| Gender | Cases | Total | Attack Rate | RR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unvaccinated | Boys | 814 | 950 | 86% | 1.00 |
| Girls | 86 | 100 | 86% | ref | |
| 1050 | |||||
| Vaccinated | Boys | 5 | 50 | 10% | 0.95 |
| Girls | 95 | 900 | 11% | ref | |
| 950 |
In our example the crude measure of effect (the risk ratio) was 4.5. The weighted measure of effect calculated with the Mantel Haenszel method is close to 1. It is obtained as follows:
The relative difference between the weighted and the crude measures of effect is more than 15% (4.5/0.99 *100 = 450%) therefore suggesting that, in our hypothetical study, vaccination is confounding (is a confounding factor for) the association between gender and disease. Had a stratified analysis been omitted, the data may lead to the conclusion that being a boy was a risk factor for the disease.
The adjusted RR 0.99 is presented, which concludes that this is the measure of association between gender and disease. This is different from effect modification, where two RRs would be presented.
Mathematically, the adjusted estimate is a weighted average of the stratum specific measures of the risk ratio. It will therefore always lie within the range of the stratum specific measures of the effect. (i.e. in the example above; 0.99 is between the range 0.95 and 1.00 - the stratum specific RRs).
For a case control study the Mantel Haenszel odds ratio (ORMH) can be computed as follows: