Objectives of Surveillance: Difference between revisions
Bosmana fem (talk | contribs) |
Bosmana fem (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
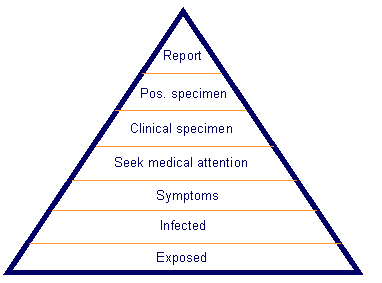
One of the first questions to be addressed in surveillance system design is that of where the data to be used should be drawn from? The answer will depend on the target population about which the surveillance outputs will be used to inform actions and on the relative ease and cost of capturing data from the potential sources available. Where the objectives of surveillance include estimating the distribution of cases within the population and changes in that distribution, then the choice of the target population and the mechanism for ascertaining cases should be guided by considerations of the representativeness of the resulting information. Many surveillance systems are based on data collection from health services, which may not have an easily defined catchment population and may include a biased subset of all cases of a particular condition (see figure 1). Many surveillance systems based on universal reporting of cases (e.g., national notification systems or national laboratory reporting schemes) are subject to significant ascertainment bias, with under-representation of asymptomatic and less severe cases and also relative over-representation of cases at the upper and lowermost ends of the age spectrum. Those responsible for surveillance systems, particularly for interpreting surveillance data, must therefore consider potential biases arising from the choice of data source and ensure that recipients of the outputs are aware of those biases. | One of the first questions to be addressed in surveillance system design is that of where the data to be used should be drawn from? The answer will depend on the target population about which the surveillance outputs will be used to inform actions and on the relative ease and cost of capturing data from the potential sources available. Where the objectives of surveillance include estimating the distribution of cases within the population and changes in that distribution, then the choice of the target population and the mechanism for ascertaining cases should be guided by considerations of the representativeness of the resulting information. Many surveillance systems are based on data collection from health services, which may not have an easily defined catchment population and may include a biased subset of all cases of a particular condition (see figure 1). Many surveillance systems based on universal reporting of cases (e.g., national notification systems or national laboratory reporting schemes) are subject to significant ascertainment bias, with under-representation of asymptomatic and less severe cases and also relative over-representation of cases at the upper and lowermost ends of the age spectrum. Those responsible for surveillance systems, particularly for interpreting surveillance data, must therefore consider potential biases arising from the choice of data source and ensure that recipients of the outputs are aware of those biases. | ||
[[File:surveillancepyramid.png|600px|frameless| | [[File:surveillancepyramid.png|600px|frameless|center]] | ||
In some situations, surveillance, particularly when its primary purpose is an early warning of outbreaks or epidemics, does not necessarily need to provide measures of disease occurrence that are representative of the general population. In the case of early warning surveillance, it is often more efficient and sensitive to focus data collection on a suitable sentinel group, e.g., surveillance in the early stages of the emergence of HIV infection in many countries focused on high-risk groups such as men who have sex with men and injecting drug users. Nevertheless, the representativeness of data reported from potential data sources needs to be considered when developing new surveillance systems and when using well-established systems. | In some situations, surveillance, particularly when its primary purpose is an early warning of outbreaks or epidemics, does not necessarily need to provide measures of disease occurrence that are representative of the general population. In the case of early warning surveillance, it is often more efficient and sensitive to focus data collection on a suitable sentinel group, e.g., surveillance in the early stages of the emergence of HIV infection in many countries focused on high-risk groups such as men who have sex with men and injecting drug users. Nevertheless, the representativeness of data reported from potential data sources needs to be considered when developing new surveillance systems and when using well-established systems. | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 18 December 2022
Objectives
The overall aim of surveillance is to provide information required to inform public health action. Although 'information for action' is often used as a meaningful synonym for surveillance, it does not help to define the purpose of surveillance any further unless we can answer the questions of 'what action?', 'what information?' and 'whose action?'.
The action may range from the management of the contacts of a single case of infection (e.g., meningococcal meningitis), to the investigation and control of an outbreak, to the development and implementation of national policy, e.g., a new immunization program or a change in national guidance on antimicrobial therapy. Actions may also include decisions to stop particular interventions on the basis that surveillance has demonstrated a lack of effect or has provided evidence of the elimination of the problem. Surveillance might also identify risk factors for disease that can be the focus of research studies into disease etiology or might identify cases for inclusion in research studies.
Because the range of public health actions that might be taken is so diverse, it is helpful to define a subset of aims that link to specific areas or types of public health action. These aims, and the associated actions, include:
- Assessing public health status
- To inform action in respect of the control and prevention of environmental hazards, exposures to potentially harmful agents, and the occurrence of disease
- Defining public health priorities
- To inform policy and planning in respect of the current and likely future impact of hazards, exposures and disease
- Evaluating programs
- To inform decisions regarding existing interventions
- Stimulating research
- To generate hypotheses and inform methodologies
Input and Outputs
One of the first questions to be addressed in surveillance system design is that of where the data to be used should be drawn from? The answer will depend on the target population about which the surveillance outputs will be used to inform actions and on the relative ease and cost of capturing data from the potential sources available. Where the objectives of surveillance include estimating the distribution of cases within the population and changes in that distribution, then the choice of the target population and the mechanism for ascertaining cases should be guided by considerations of the representativeness of the resulting information. Many surveillance systems are based on data collection from health services, which may not have an easily defined catchment population and may include a biased subset of all cases of a particular condition (see figure 1). Many surveillance systems based on universal reporting of cases (e.g., national notification systems or national laboratory reporting schemes) are subject to significant ascertainment bias, with under-representation of asymptomatic and less severe cases and also relative over-representation of cases at the upper and lowermost ends of the age spectrum. Those responsible for surveillance systems, particularly for interpreting surveillance data, must therefore consider potential biases arising from the choice of data source and ensure that recipients of the outputs are aware of those biases.
In some situations, surveillance, particularly when its primary purpose is an early warning of outbreaks or epidemics, does not necessarily need to provide measures of disease occurrence that are representative of the general population. In the case of early warning surveillance, it is often more efficient and sensitive to focus data collection on a suitable sentinel group, e.g., surveillance in the early stages of the emergence of HIV infection in many countries focused on high-risk groups such as men who have sex with men and injecting drug users. Nevertheless, the representativeness of data reported from potential data sources needs to be considered when developing new surveillance systems and when using well-established systems.
The purpose of surveillance is to provide information for action, and as such, the design of a surveillance system should be shaped by the information requirements (surveillance system outputs) of those responsible for taking the control and prevention activities that is to be informed by the system. Typically surveillance outputs will be in the form of tables or graphs showing counts or rates of cases/events or proportional morbidity or mortality, categorized by demographic, geographic, or other risk factors. These may be accompanied by statistical measures of trend or exception, and increasingly geographical information systems are being used to analyze and present surveillance outputs. Surveillance outputs may also take the form of listings of cases requiring public health follow-up or be data files that can be subject to additional analyses or used in record linkage by the recipients.
It is not always possible, usually for reasons of practicability or cost, to provide exactly the information that policymakers, service planners, or health service providers might require, and often the choice of outputs is a balance of what it is possible to provide within the constraints of resources and data availability and what is actually required (see box for example).
Those responsible for controlling HIV/AIDS would ideally like surveillance systems to provide information on the incidence of infection. However, the mild and non-specific nature of HIV seroconversion illness means that true 'incident' cases are rarely detected, and so direct measures of incidence from surveillance based on clinical service testing are not possible (although this could be achieved through the long-term study of defined cohorts, with regular testing). Surveillance systems have been developed that can provide proxy measures of incidence or at least provide information on how recently detected infections are likely to have been acquired. This has largely been done by making use of advances in laboratory techniques, such as developing routine assays of CD4 cell counts (higher counts at the time of the first HIV-positive test indicate more recent infection) and 'detuned' HIV assays.
The frequency and timeliness of outputs are particularly important in communicable disease surveillance. Early identification of outbreaks or epidemics is required to mount effective measures to interrupt transmission or prepare other responses. This need for frequent and timely outputs has important consequences for the operation of surveillance systems, such as continuous data capture systems, rapid data transfer and analysis, and the human and information technology resources required to support those processes.